Metal Marking Methods – Analysis & Equipment Recommendations
Metal marking is an essential process in various industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and medical equipment production. Whether for identification, branding, traceability, or compliance, different marking technologies cater to specific needs. This article will explore five common metal marking methods, compare their advantages and limitations, and provide insights into choosing the best method based on material, application, and cost considerations.

Exploring Five Common Metal Marking Technologies
Laser Marking Technology
Principle: Laser marking utilizes a high-energy laser beam to alter the surface of the metal, creating permanent marks through oxidation, engraving, or annealing. The laser interacts with the metal surface, producing high-contrast marks without direct contact.
Advantages
- High precision and resolution, suitable for intricate designs.
- Permanent and wear-resistant markings.
- Non-contact process, minimizing mechanical damage.
- Works on a variety of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium.
- High-speed processing, suitable for mass production.
Pneumatic Dot Peen Marking

Principle: Pneumatic dot peen marking involves a vibrating carbide or tungsten stylus that strikes the metal surface repeatedly, creating a series of small dots that form characters, numbers, or logos. This method produces deep and durable engravings.
Suitable Applications
- Ideal for marking serial numbers, VIN codes, and barcodes.
- Used in heavy industries, including aerospace, automotive, and machinery manufacturing.
- Works well on hard metals such as steel and iron.
Electrochemical Etching
Principle: This method uses an electrolyte solution and an electric current to remove metal ions from the surface, creating a mark. A stencil defines the shape of the mark, and a low-voltage current facilitates the etching process.
Industry Applications
- Common in the medical industry for marking surgical instruments.
- Used in the aerospace industry for part identification.
- Suitable for marking tools, knives, and stainless steel components.
Inkjet Marking Technology
Principle: Inkjet marking involves spraying tiny droplets of ink onto the metal surface to create a temporary or permanent mark. This is a non-contact marking method that allows for variable data printing, such as expiration dates and QR codes.
Limitation Analysis
- Requires consumables (ink cartridges), leading to ongoing costs.
- Less durable compared to engraving or etching methods.
- Not ideal for harsh environments where markings need to withstand abrasion or chemicals.
Thermal Transfer Marking
Principle: Thermal transfer marking applies heat and pressure to transfer ink or resin from a ribbon onto a metal surface. This method creates high-resolution prints that adhere firmly to the metal.
Emerging Trends
- Increasing use of durable resin-based ribbons for enhanced longevity.
- Development of hybrid systems combining thermal transfer with protective coatings.
- Rising adoption in the electronics and medical sectors for high-precision labeling.
Comparative Analysis of Metal Marking Technologies
| Marking Method | Durability | Precision | Speed | Cost | Material Suitability | Consumables Required | Best For |
| Laser Marking | High | High | Fast | High | Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium | No | Industrial parts, branding, fine details |
| Pneumatic Dot Peen | Very High | Medium | Medium | Medium | Steel, iron, alloys | No | VIN codes, deep engraving, heavy industries |
| Electrochemical Etching | Medium | High | Fast | Low | Stainless steel, conductive metals | Yes (electrolyte, stencils) | Medical tools, aerospace components |
| Inkjet Marking | Low | Medium | Very Fast | Low | Various metals | Yes (ink) | Date codes, batch numbers, packaging |
| Thermal Transfer | Medium | High | Fast | Medium | Aluminum, coated metals | Yes (ribbon) | Electronics, medical instruments |
How to Choose the Right Metal Marking Method?
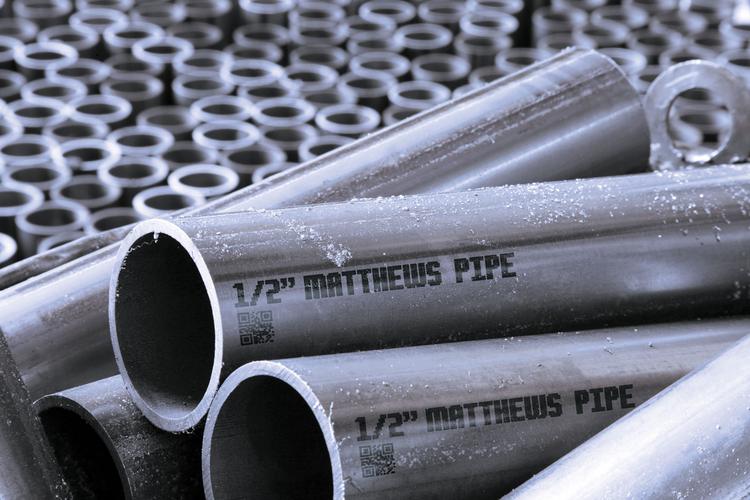

Material Compatibility
Different marking technologies work best with specific metals. For example:
- Stainless Steel & Aluminum: Laser marking, electrochemical etching.
- Hard Metals (Steel, Iron): Pneumatic dot peen for deep engraving.
- Coated or Painted Metals: Thermal transfer or inkjet marking.
Application-Specific Requirements
- Permanent, high-contrast marks: Laser marking or electrochemical etching.
- Deep engraving for harsh environments: Pneumatic dot peen.
- Variable data printing (expiration dates, serial numbers): Inkjet or thermal transfer.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
- Laser marking has a higher initial cost but requires minimal maintenance.
- Pneumatic dot peen is cost-effective for durable marking but may have slower processing speeds.
- Electrochemical etching is low-cost but requires consumables (electrolytes, stencils).
- Inkjet marking is inexpensive initially but has ongoing ink costs.
- Thermal transfer provides high-quality prints but requires ribbons.

Equipment Recommendations
For businesses seeking reliable and high-performance metal marking solutions, investing in the right equipment ensures efficiency and long-term cost savings. If you’re looking for customized solutions, contact us to explore our range of engraving machines for metal tags tailored to your industry needs.
Benchtop Pneumatic Dot Peen Engraver
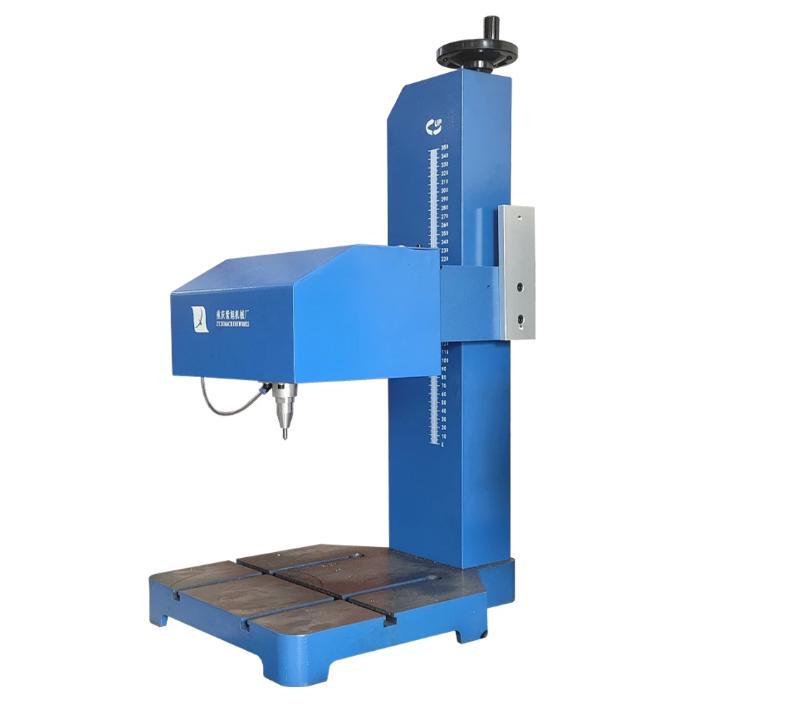

Our benchtop pneumatic dot peen marking machines offer high marking consistency for smaller parts with custom fixtures and integrate with MES for automated online coding. They are widely used for marking metal pipes, flanges, gears, gas cylinders, and silverware. Common applications include machinery nameplates and VIN marking on separate plates. We provide various benchtop systems and automated/manual fixtures for precise positioning and consistent quality, along with rotary, multi-axis robot, and fully customized fixturing for complex surfaces.
Fiber Laser Marking Machine
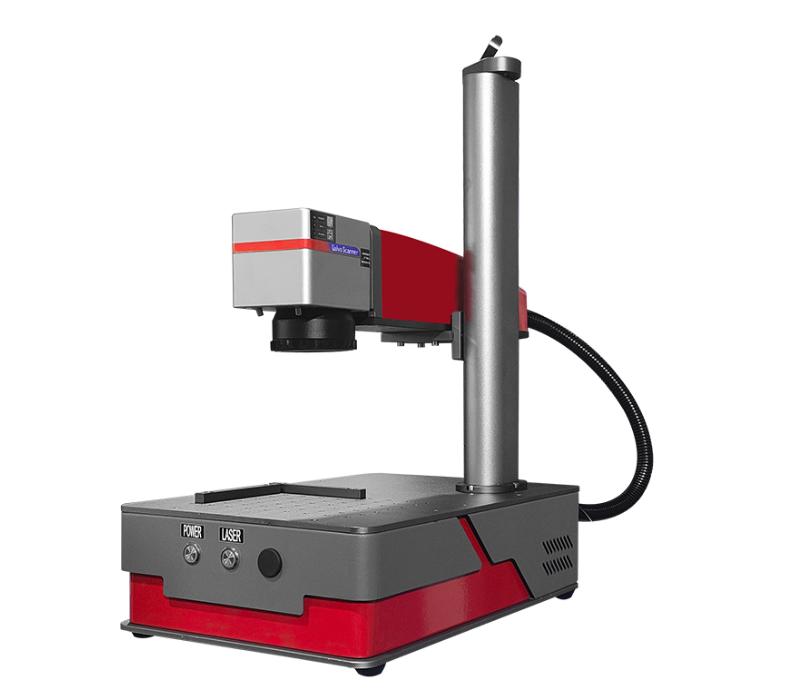

Fiber laser marking machines utilize highly energy-efficient fiber laser sources, often achieving a photovoltaic conversion rate of 38% or greater. This technology provides an affordable solution for marking a wide range of metals and certain plastics. Our comprehensive selection of fiber laser markers includes compact, handheld portable units, fully automated 3D flying cabinet models equipped with CCD cameras and dynamic focus, and fully customized machines engineered to meet specific customer requirements for optimal performance.
Choosing the right metal marking method depends on factors like material type, marking durability, precision needs, and cost considerations. Laser marking stands out for its precision and permanence, while dot peen excels in deep engraving for industrial applications. Electrochemical etching is ideal for delicate medical instruments, whereas inkjet and thermal transfer are best suited for variable data printing.
Recommended Products